A graphics card, or GPU for short, is a special purpose hardware piece in a computer that is used for rendering images, videos, and animations. It plays a pretty important role in playing games, video editing, 3D modeling, and running complicated simulations. Here's a little explanation of what it is and how it works:
What Is a Graphics Card?
A graphics card is basically a mini-computer inside your computer. It comprises the following components:
- GPU (Graphics Processing Unit): The "brain" of the graphics card, responsible for performing calculations related to image rendering.
- VRAM (Video RAM): Specialized memory used to store image data, textures, and frame buffers for fast access during rendering.
- Cooling System: Fans and heatsinks to keep the GPU cool while it processes intense tasks.
- Power Supply Interface: Connected to the computer's power supply for sufficient power.
- Output Ports: Connects the card to monitors using HDMI, DisplayPort, or VGA
How's a graphic card look like
 |
| RTX |
How It Works
When a computer has to draw an image or video, here's how the process works:
The CPU:
The CPU sends instructions to the graphics card, which lets the graphics card know what it should draw.
GPU Processing: The GPU proceeds to calculate millions of calculations to draw shapes, colors, lighting, shadows, and textures in the image.
Example: In the case of a 3D game, the GPU will compute the position of the objects within, apply textures as well as simulate lighting effects.
VRAM Usage: The GPU keeps temporary data in VRAM, including Rendered frames, game textures, or video buffers, so operations remain smooth and not laggy.
Rendering Frame: The GPU reduces the raw data into a visible format, and it prepares the frame.
These frames are displayed in sequence at a certain refresh rate. For example, the rate 60Hz means that 60 frames per second are sent
.
Output to the Display:The image or video is rendered by the graphics card and passed to the monitor through an output port.
Types of Graphics Cards
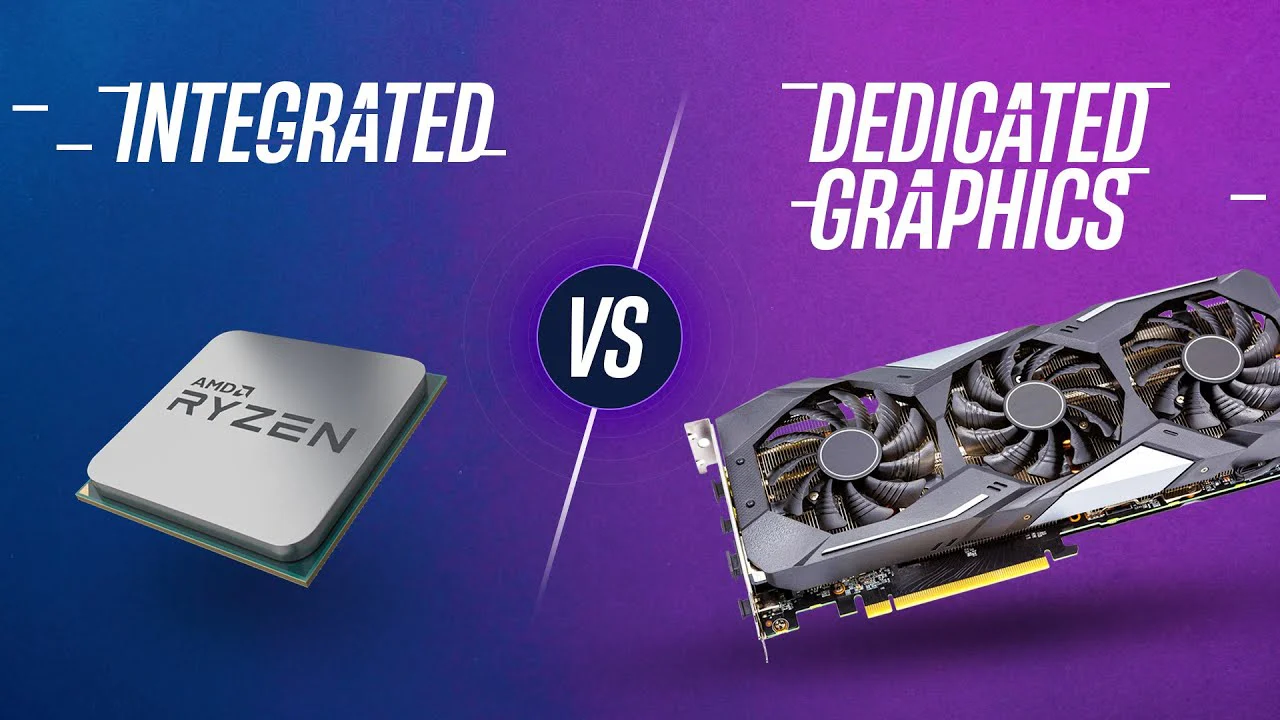
Integrated Graphics: Graphics that are inside the CPU.
For surfing, web browsing, and light video playback are their proper applications.
Example-Intel UHD Graphics
Dedicated Graphics: A dedicated card that has an independent GPU and VRAM.
Gaming, professional 3D work, and AI usage is best suited with this.
Example- NVIDIA GeForce RTX or AMD Radeon RX series.
Modern Applications of Graphics Cards
Gaming: Real-time rendering for high-quality visuals.
Video Editing: Enables faster rendering and effects processing.
AI and Machine Learning: Large models can be trained in parallel, hence used.
3D Modeling and Rendering: Manages detailed graphics for architects, designers, and animators.
ROLE OF GPU
1. Graphics Rendering
Primary Role: The primary role of the GPU is to render graphics for display on a monitor. These include:
2D and 3D Rendering: Creating images, animations, and visual effects in games, movies, and software.
Lighting and Shading: Simulating realistic lighting, shadows, and textures.
Resolution and Frame Rate: Supports high resolutions, for example 4K, 8K and smooth frame rates, such as 60 FPS, 120 FPS.
2. Gaming
- In gaming, the GPU renders 3D environments, animations, and textures in real time.
- It processes complex tasks like physics simulations, motion blur, and advanced lighting techniques (e.g., ray tracing).
3. Video Processing
- GPUs handle video decoding and encoding tasks, which are essential for:
- Playing high-definition videos smoothly.
- Streaming content.
- Video editing and rendering, where effects and transitions are applied efficiently.
4. Parallel Computing
That is what makes GPUs ideal for parallel processing: unlike with CPUs, which have fewer cores but more powerful ones, thousands of smaller cores exist within them.
AI and Machine Learning: Training and inference for neural networks, such as in deep learning models.
Scientific simulations: Processing large datasets for weather modeling, physics simulations, or bioinformatics.
Cryptocurrency Mining: Solving cryptographic problems for blockchain verification
5. Productivity and Professional Applications
GPUs are high utilisers in professional fields
3D Modeling and Animation: Rendering in most CAD software, Blender, Maya, etc.
Architectural Design: Real-time rendering of building models
Virtual Reality (VR): Rendering realistic environments in real time
.
6. Accelerating General Computation (GPGPU)
GPGPU (General-Purpose computing on GPUs): For non-graphic applications that require the benefit of parallel processing
Examples - Data analysis, financial modelling, and heavy mathematical calculations.
7. Image Processing
GPUS make photo editing, application of filters, and real-time image recognition in cameras and software possible.
8. Fueling Advanced Graphics Display
GPUs support following advanced display features:
Multi-monitor setups.
High Dynamic Range (HDR) visuals.
Variable refresh rates (e.g., NVIDIA G-Sync, AMD FreeSync).





0 Comments